Ch 7 - Structural organization in animals

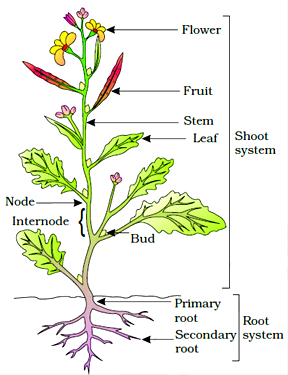
CHAPTER-07 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION IN ANIMALS In multicellular organism a group of similar cells along with intercellular substances perform a specific function. Such organization is called tissue. Epithelial Tissue : This tissue provides covering or lining for some part of the body. Cells are compactly packed without intercellular space. Simple epithelium is composed of single layer of cells and function as lining of body cavities, ducts and tubes. The compound epithelium consists of two or more than two layers of cells and has protective function. The squamous epithelium is made up of single layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. They are present in lining of blood vessels, air sacs of lungs. Cuboidal epithelium is made up of single layered cube-like c...